Vivint Solar, owned by the Blackstone Group, set its IPO terms to offer 20.6 million shares at $16 per share. That would give the Provo, Utah-based installer and financier a market cap of more than $1.5 billion. Goldman Sachs, BofA Merrill Lynch and Credit Suisse are serving as lead underwriters.
It's an important event in the U.S. solar industry as Vivint Solar, the No. 2 installer in the U.S., opens the residential solar market to further investment and growth.
SolarCity and Vivint Solar combined to install 51 percent of all U.S. residential PV in the second quarter of the year, according to GTM Research's U.S. PV Leaderboard. The U.S. added 247 megawatts of residential PV, making it the segment's second-largest quarter ever.
SolarCity, with a market cap of $5.67 billion, continues to lead the market, installing 36 percent of the U.S. residential total, up from 28 percent in the first quarter of the year. According to SolarCity's second-quarter earnings call, the financier and installer added 30,000 customers in the quarter, installing PV at a pace of 1.2 megawatts per day.
SolarCity went public in December 2012, priced at $8 per share and raised $92 million.
Soon-to-be-public Vivint installed 15 percent of the country's residential PV, up from 8 percent in the first quarter. GTM Research Analyst Nicole Litvak has noted that Vivint is active in six states and is the leading residential installer in New York and Massachusetts.
"Vivint is currently growing faster than SolarCity and is on track to more than double installations this year over 2013," said Litvak. "Nonetheless, SolarCity is poised to remain the top installer for the foreseeable future."
"Investors in solar want fast growth and yield. Residential solar has the fastest growth and best yields," said Nat Kreamer, CEO of solar finance platform Clean Power Finance. "Vivint Solar going public is another example of the value of residential solar."
Nancy Pfund, managing partner at DBL Investors (an early investor in SolarCity), notes, "The stock market will welcome this IPO, as a growing number of people want to build solar portfolios, and to do that, they need more high-quality names. Solar is still only at 1 percent penetration. We need several strong companies to transform the energy market from one that is fossil-based to one that fits our planet's need for a low-carbon future. Just as at the beginning of the 20th century, there emerged hundreds of oil companies that over the decades turned into the Exxons and Chevrons and BPs of the world, now we are just beginning to experience a clean energy version of this metamorphosis. There is ample room for companies like SolarCity, Vivint, and others to thrive as we pass the energy torch from the 20th to the 21st century."
The IPO hopeful is the solar integrator and PPA financier unit within Vivint, one of the largest home-alarm system and home automation companies, which was acquired by Blackstone for more than $2 billion in September 2012. Vivint has more than 675,000 customers for its home security and automation services across the country.
Here's the updated SEC S-1 IPO registration document. Some of GTM's previous reporting on the company's financials follows.
Tidbits from the S-1
-
Vivint is growing fast -- and losing money fast as well.
-
Vivint Solar has installed a total of 129.7 megawatts of solar at more than 21,900 homes in seven states, with an average solar system size of approximately 5.9 kilowatts.
-
The company has raised nine investment funds to which banks have committed to invest approximately $443 million. This will allow Vivint to install PV systems of approximately $1.1 billion in value.
-
Vivint Solar also has LOIs from three financial institutions in amounts totaling up to $250 million, enough to fund approximately 111 megawatts of future rooftop installations.
-
The company notes that "the recent acquisition of Zep Solar, Inc., who sold us virtually all of the racking systems used in our hardware in 2013, by one of our competitors and the resulting limitation in our ability to acquire Zep Solar, Inc. products required us to redesign certain aspects of our systems to accommodate alternative racking hardware."
| 2012 | 2013 | First 6 months of 2014 | |
| Systems Installed | 2,669 | 10,521 | 8,625 |
| Megawatts Installed | 14.4 MW | 58 MW | 56.8 MW |
| Revenue | $5.8 M | $8.6M | |
| Net Loss | $16.7M | $56.4M | $76.1M |
Here are some of the points that caught the eyes of our analysts:
- The company had this to say about its relationship with Zep: "We have successfully transitioned away from using racking systems procured from Zep Solar, Inc., although we currently have a limited inventory remaining in certain of our markets which we are using primarily as replacement parts on service calls. Once that inventory is gone, we will no longer use any racking systems from Zep Solar, Inc. We believe that our new racking system providers will be able to meet all of our needs going forward, and we do not expect any interruption to our business as a result of, or following, this transition."
- Average FICO score across all Vivint customers: 750
- "Most of our current customer contracts contain price escalators ranging from 2.9% to 3.9% annually."
- Assumed O&M and asset management costs over the lifetime of the system is $0.60 per watt to $0.80 per watt
- Solmetric acquisition was $12.2 million.
- Five funds are using partnership-flip, and four funds are using inverted leases.
- Sales turnover is high: "43% of the sales force on January 1, 2013 were no longer providing services to us by the end of the year."
GTM Research's Nicole Litvak provided some analysis on Vivint Solar earlier this month, which is excerpted below.
Regional presence
Surprisingly, Vivint is active in far fewer markets than other national installers such as SolarCity, Sungevity, and Solar Universe (which are active in a dozen or more states). Instead, Vivint has put all of its sales efforts into just six states, not including its recently announced expansion to Arizona. The large gap between SolarCity and Vivint is most drastic in California, but Vivint has beat the national leader in New York and Massachusetts for the past several quarters.
FIGURE: Vivint's State-by-State Market Share, 2013
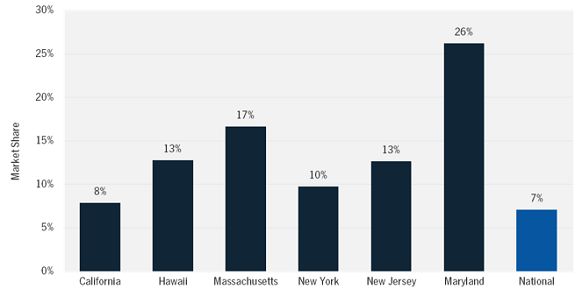
Source: GTM Research U.S. PV Leaderboard
Sales strategy
Vivint Solar is well known for its sales model, which was adopted from its parent company Vivint Inc. and consists almost entirely of door-to-door soliciting (in addition to referrals). This strategy may explain the company’s slow expansion to new states, as it requires hiring a large sales team. The map below shows just how concentrated the door-to-door sales method must be, even when implemented in a small state like Massachusetts. Vivint’s acquisition of Solmetric was meant to further increase the efficiency of its door-to-door sales by allowing sales reps to take roof measurements, create a preliminary design, and potentially close the sale on the first visit. The installer even forgoes state incentives in some cases to speed up the installation process.
FIGURE: Vivint Solar Installations in Massachusetts, Jan. 2012-June 2013
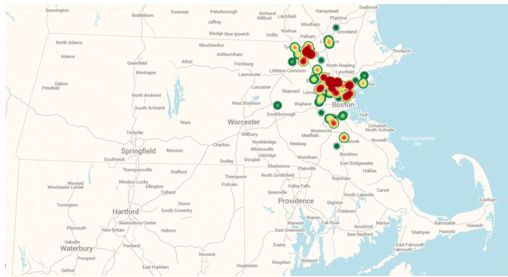
Source: GTM Research report U.S. Residential Solar PV Customer Acquisition
Suppliers
Vivint’s overall business model involves simplifying as many areas of its operations as possible, such as using one primary sales method. Another key area to which this applies is its suppliers. Vivint Solar’s top module suppliers in 2013 were Trina Solar (also the leading supplier to SolarCity) followed by Yingli Solar and Canadian Solar -- three of the top five suppliers to the U.S. residential solar market, according to the GTM Research U.S. PV Leaderboard. The installer also uses just one inverter supplier, Enphase Energy, partly due to the flexibility that microinverters offer for making last-minute changes during installation. Just last week, the two companies signed a three-year strategic agreement to continue this supply relationship. Vivint Solar used only Zep Solar mounting structures until that supplier was acquired by SolarCity.
FIGURE: Module Suppliers to Vivint Solar, 2013
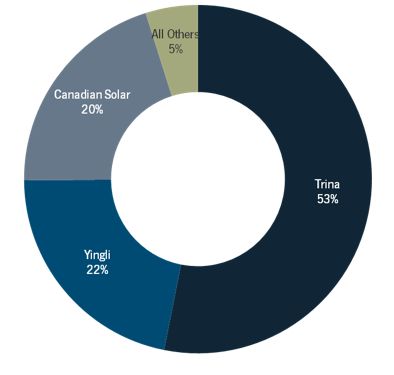
Source: GTM Research U.S. PV Leaderboard
Financing strategy
Vivint Solar is one of the industry’s two completely vertically integrated financiers, meaning it both finances and installs systems. Its consumer financing options are limited, in line with the rest of its streamlined operations. Originally, the installer only offered power-purchase agreements, but it has recently added a lease option. Vivint Solar is the only leading financier that has shown no signs of intending to add a loan product.



